|
1. Background
n
Increase of interest in
stereoscopic 3D video
n
Concerns on 3D image
safety issues
Visual discomfort and
visual fatigue
Excessive screen
disparity, fast motion, and stereoscopic distortions
n
Needs of visual comfort metric and safety
guidelines
2. Proposed Attention Model-based Visual Comfort Metric
for Stereoscopic Videos
n
We employ 3D content
analysis and visual attention model to quantify causes of visual fatigue
n
Visual comfort (VC)
metric based on contents and visual
attention model
Motion and depth statistics of visual importance regions,
where human subjects pay more attention, are likely to play an essential
role in determining overall VC score.
Human attention model in
HVS

Fig. 1. The Proposed Attention Model-based Visual Comfort
Metric for motion characteristics [1].
3. Visual Importance Region
Detection for Attention Model-based Visual Comfort Metric
n
Perceptually significant
regions
Combination of image
attention model and motion attention model
Saliency-based measures
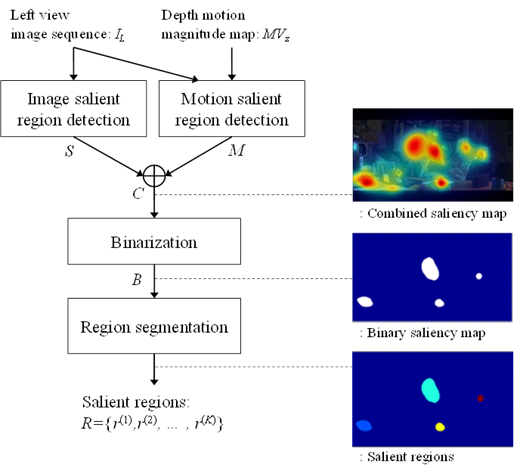
Fig. 2. Perceptually significant region extraction [1].
4. Perceptually
Significant Motion Features
n
Perceptually significant
motion features
Planar motion
Horizontal motion
velocity (in degree/sec)
Vertical motion velocity
(in degree/sec)
In-depth motion velocity
(in degree/sec)
5. Experiments:
subjective test
n
Experimental environment
Stereoscopic display:
40 half mirror type (linear polarization)

Fig. 3. Experimental environment [1].
n
Subjects
Number of subjects (non experts) recruited for subjective assessments:
40 for the experiment of
visual comfort model construction with synthetic video
20 for the validation
experiment with real stereoscopic video (3 subjects were rejected by the stereofly test and the screening test of ITU-R BT
500-11)
The subjects were
recruited under approval of KAIST IRB (Institutional Review Board)
All subjects had normal
or corrected vision and a minimum stereopsis of 60 arcsec
(in stereo fly test)
Aged between 20 and 37
years
n
Visual Stimulus used for
visual comfort model construction of motion stimuli
Object type: gray meteor
Field size of object: 2 degree
Background: Mid-gray (Illuminant D65, 50 cd/m2)
Foreground: Dark-gray (25 cd/m2)

Fig. 4. Visual Stimulus used for visual comfort model
construction of motion stimuli [1].
n
Visual comfort model for
motion characteristics
Mean of median rating scores to remove outliers
Fitting of the psychometric functions obtained by subjective
assessments
We obtained the fits to three log models in terms of movement
velocity for each directional motion (in agreement with Fechners log
law)
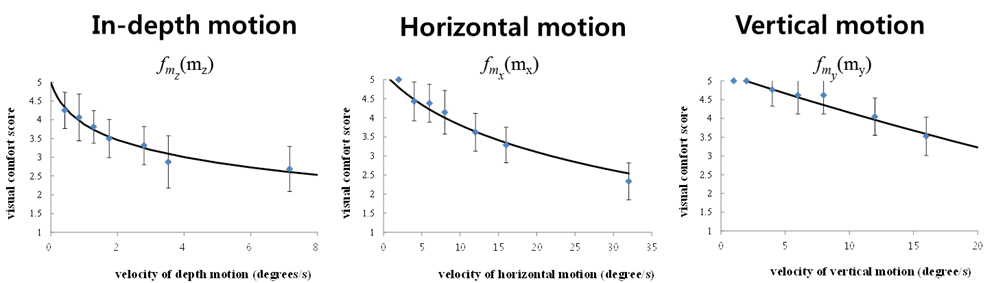
Fig. 5. Visual comfort model for motion characteristics
[1].
n
Evaluation of visual
comfort metric for motion characteristics
Number of real stereoscopic videos: 40
36 natural scenes captured using a 3D digital camera with dual
lenses (Fujifilm FinePix 3D W3) and 4 MPEG 3D
video test sequences
Various motion speed and motion directions (horizontal, vertical,
and depth motions)
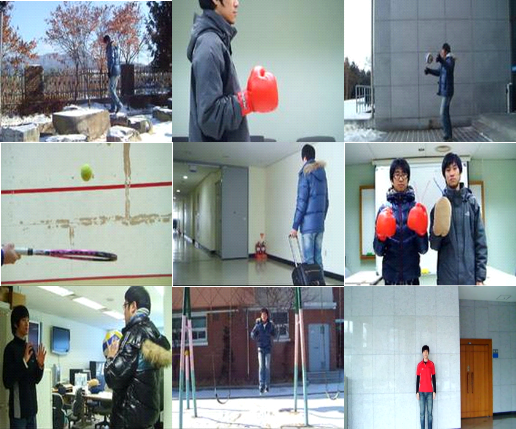

Fig. 6. Stereoscopic videos for evaluation of visual
comfort metric [1].
n
Evaluation results of
visual comfort metric for motion characteristics
The proposed attention model-based approach outperforms the global
statistics-based approaches
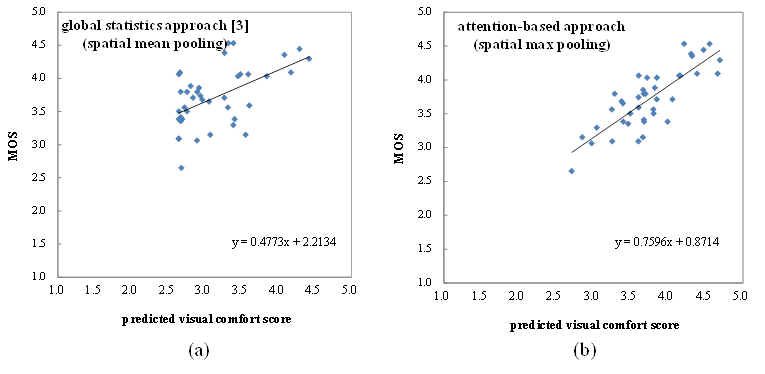
Fig. 7. Scatter plot between MOSs and predicted visual
comfort scores [1].
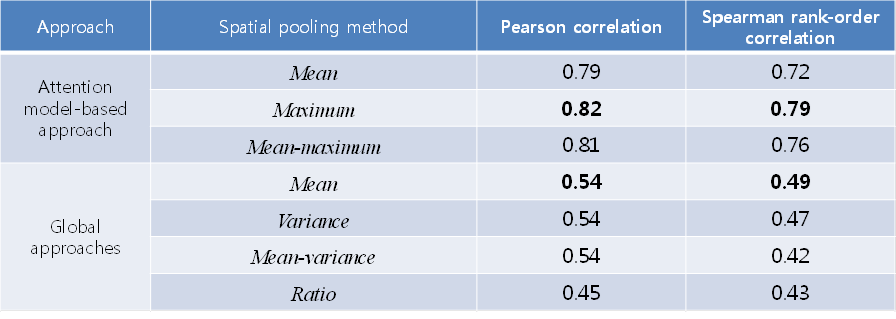
Table 1. Quantitative results of prediction performance:
Correlation measure between subjective MOSs and predicted visual comfort
scores [1].
|