Active Media
Introduction Contents
1.1. Universal Multimedia Access
Universal Multimedia Access (UMA), a new trend in multimedia communication, is the technology, which relates to the ability to access rich multimedia content regardless of the client device, client device capabilities, network bandwidth or resource. The relevance of universal access is supported by many forecasts that predict a tremendous and continuing growth in the number of pervasive computing device, such hand-held computers, personal digital assistant(PDAs), smart phone, automotive computing device, wearable computers, and so forth. This can be achieved by pre-storing variations of the original content or by creating on-the-fly adaptations of the original content tailored to the system specification.
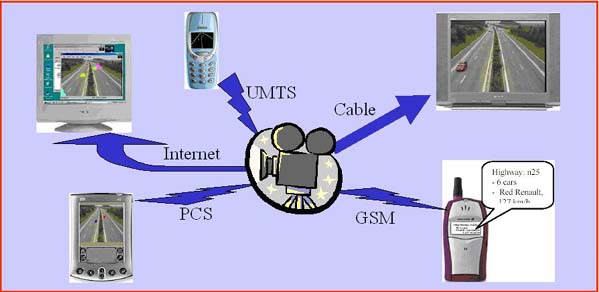
Figure 1. A comprehensive solution for accessing the contents at any place and any time
¡°Active media¡± means that content can understand its delivery or consumption environments and adapt itself based on the awareness about the content itself. It is necessary that users can consume various types of contents transparently and augmently under the heterogeneous consumption environment. In other words, can actively adapt itself according to various environments including user characteristics and various devices such as PDA, PC, Mobile phone, HDTV, etc
Due to high diversity and heterogeneity of user characteristics, client devices and network connections, adaptation system and media itself need to have intelligence according to user and consumer environment.
¡°Active Room¡± where user can consume active media according to environment characteristics.
![]() Adaptation system
Adaptation system
An adaptation system should provide the optimal content version among variations or generate that version in real-time according to the context information including usage environment descriptions.
![]() MPEG-21
MPEG-21
The Multimedia Framework, which is being standardized for the delivery and consumption of multimedia contents across a wide range of networks and devices.
![]() The fundamental items
The fundamental items
- User Characteristics : specify user preferences to media format and presentation.
- Terminal Capabilities : specify the capabilities of terminals
- Network Characteristics : specify the capabilities and conditions of a network
- Natural Environment Characteristics : specify location, time of a user in a given environment
- Digital Item Resource Adaptation Tools : target the adaptation of resources in a digital item.
- Session Mobility : specify how to transfer the state of digital items from one user to another
![]() Decision Engine
Decision Engine
It take into account all information about multimedia content, network characteristics, device capabilities and user preferences and finally provide the best presentation to user given a certain set of constraints
![]() Resource Level Tools
Resource Level Tools
It includes transcoding algorithms for resources or contents based on active media. It must support bitrate upscaling or downscaling, format conversion, and modality conversion
![]() Constraints Detection and Exchange
Constraints Detection and Exchange
It collect efficiently the information of network characteristics, device capabilities, user preferences and session so as the decision engine can select the most suitable transcoding choices for any instant contexts.
1.4. Related Adaptation Technology
![]() Visual information adaptation: that allows users to have choices on presentation
qualities of different contents.
Visual information adaptation: that allows users to have choices on presentation
qualities of different contents.
![]() Modality Conversion: that allows users to have choices on the
modalities of adapted contents.
Modality Conversion: that allows users to have choices on the
modalities of adapted contents.
![]() Color preference adaptation: that adapts the colored contents so as
color-deficiency users can have a proper perception of the information.
Adaptation is performed respectively for severe color
vision deficiency (dichromats) and for mild
color vision deficiency (anomalous trichromats) according to the
description of user characteristics about
color vision variations.
Color preference adaptation: that adapts the colored contents so as
color-deficiency users can have a proper perception of the information.
Adaptation is performed respectively for severe color
vision deficiency (dichromats) and for mild
color vision deficiency (anomalous trichromats) according to the
description of user characteristics about
color vision variations.