- Overview of Content based Indexing & Retrieval System
In the service of multimedia service, the requirement of Multimedia Indexing Technology is increasing to retrieve and search for interesting data from huge Internet. Since the traditional retrieval method, which is using textual index, has limitation to handle the multimedia data in current Internet, alternatively, the more efficient representation method is needed.
In standard manner, the research for method of feature extraction and multimedia indexing of Audio/Video contents and Images based on MPEG-7 Standard is performing. The feature of content is extracted using MPEG-7 XM(eXperimental Module) for representation of multimedia content. The indexing and matching algorithm using extracted features is researched to support the efficiency of searching and retrieval. To achieve the objectives, MPEG-7 system is being developed, including the user interface and the efficient way for delivering of multimedia description in the mobile Internet environment is also being performed.
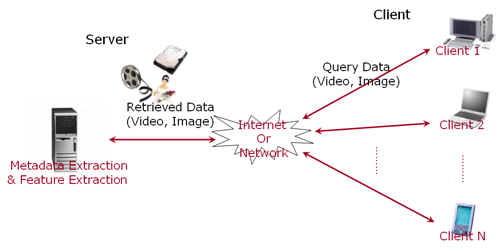
Fig. 1. Overview for Contents based Retrieval and Indexing System
As shown in Fig. 1, the basic image retrieval application system for MPEG-7 content based indexing is consisted server-client system. In client, the multimedia consumers can input the image or video as their query. Then, the query image is analyzed to be MPEG-7 visual descriptor, and the matching modules find the best answers for users' query.
- Traditional Concepts for Contents based Indexing
Recent advances in computer, telecommunications, and consumer electronics industries have brought huge amount of multimedia information to a rapidly growing audience. More and more digital audio and video data are made available over the Internet. Traditional TV broadcast is moving into the digital and interactive era.
People are starting to get high-speed network connections via DSL and cable modem. Multimedia content provides rich information to consumers, but also poses challenging problems of management, delivery, access, and retrieval because of its data size and complexity.
In recent years, there has been active research trying to address these problems and make multimedia information efficiently accessible to the user. Researchers from signal processing, computer vision, and other related ?elds have generated a large body of knowledge and techniques. These techniques generally fall into one of the following research areas.
- Video indexing: research in this area aims at creating compact indices for large video databases and providing easy browsing and intelligent query mechanisms. Potential applications include multimedia databases, digital libraries, and web media portals.
- Video filtering and abstraction: research in this area tries to generate an abstract version of the video content that is important or interesting by extracting key portions of the video. This can be used for personalized video delivery, intelligent digital video recording devices, and video summaries for large multimedia archives.
- Audio indexing and analysis: research in this relatively new area includes audio classification, audio indexing and retrieval, music retrieval, etc. Efforts have also been made in combining audio information with visual information to help index and analyze video content.
- Introduction to MPEG-7
MPEG-7 is an ISO/IEC standard developed by MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group), the committee that also developed the successful standards known as MPEG-1 (1992) and MPEG-2 (1994), and the MPEG-4 standard (Version 1 in 1998, and version 2 in 1999). The MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 standards have enabled the production of widely adopted commercial products, such as Video CD, MP3, digital audio broadcasting (DAB), DVD, digital television (DVB and ATSC), and many video-on-demand trials and commercial services. MPEG-4 is the first real multimedia representation standard, allowing interactivity and a combination of natural and synthetic material, coded in the form of objects (it models audiovisual data as a composition of these objects). MPEG-4 provides the standardized technological elements enabling the integration of the production, distribution and content access paradigms of the fields of interactive multimedia, mobile multimedia, interactive graphics and enhanced digital television.
The MPEG-7 standard, formally named ¡°Multimedia Content Description Interface¡±, provides a rich set of standardized tools to describe multimedia content. Both human users and automatic systems that process audiovisual information are within the scope of MPEG-7.
MPEG-7 offers a comprehensive set of audiovisual Description Tools (the metadata elements and their structure and relationships, that are defined by the standard in the form of Descriptors and Description Schemes) to create descriptions (i.e., a set of instantiated Description Schemes and their corresponding Descriptors at the users will), which will form the basis for applications enabling the needed effective and efficient access (search, filtering and browsing) to multimedia content. This is a challenging task given the broad spectrum of requirements and targeted multimedia applications, and the broad number of audiovisual features of importance in such context.
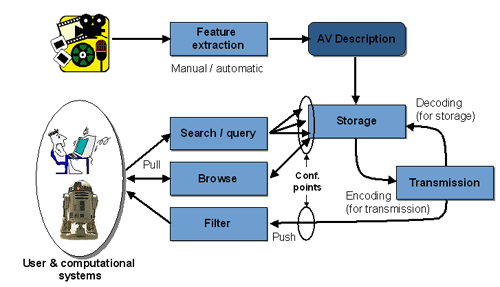
Fig. 2. Abstract representation of possible application using MPEG-7
Figure 2 explains a hypothetical MPEG-7 chain in practice . From the multimedia content an Audiovisual description is obtained via manual or semi-automatic extraction. The AV description may be stored (as depicted in the figure) or streamed directly. If we consider a pull scenario, client applications will submit queries to the descriptions repository abd will receive a set of descriptions matching the query for browsing (just for inspecting the description, for manipulating it, for retrieving the described content, etc.). In a push scenario a filter (e.g., an inteligent agent) will select descriptions from the available ones and perform the programmed actions aftyerwards (e.g., switching a broadcast channel or recording the described stream). In both scenarios, the all the modules may handle descriptions coded in MPEG-7 formats (either textual or binary), but only at the indicated conformance points it is required to be MPEG-7 conformant (as they show the interfaces between an application acting as information server and information consumer).
- MPEG-7 Visual Descriptors: Standardized Descriptors
|
|
- Contents based Indexing & Retrieval System
The contents based indexing & retrieval system is consisted of several modules like in Fig. 3. The images and videos are collected by "Meta Serach Engine" from published web pages. The MPEG-7 visual features, color and texture in this system, are extracted from the populated images. And the extracted features are stored to database. When users in client input the query as image file or textual type, the characteristics of images are extracted to match the already consisted feature database.
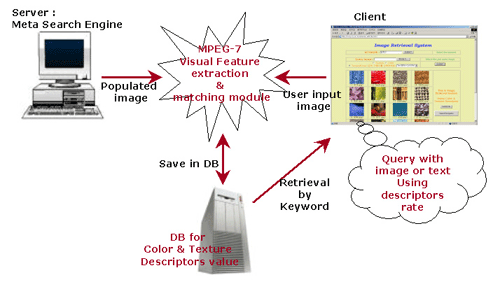
Fig. 3. General Contents based Retrieval System
In Fig. 4, the query style can be determined by user's interest. One type is textual type and another is image type. Each method can compensate for others. And user can control the weighting value through user interface to obtain more interesting images.
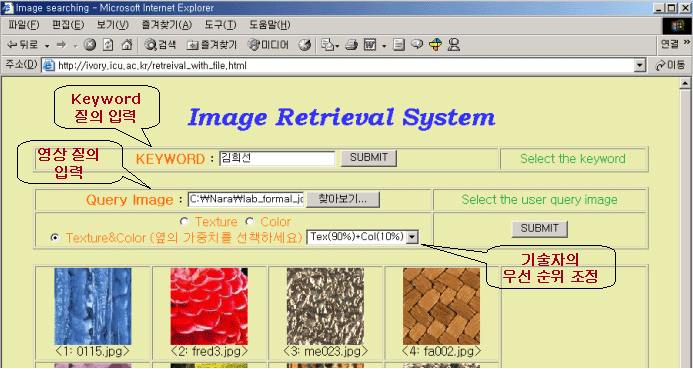
Fig. 4. Query Input: Textual Format, Image Format
The matching algorithm can be defined as Fig. 5. The MPEG-7 color and texture features of query image are extracted. And distances for each descriptor between query image and images in database are measured. After that, with weighting factors, the final distance are extracted and the final rank of results is determined. And the result of query is like Fig. 6.

Fig. 5. Ranking and Similarity Mating with Color and Texture features
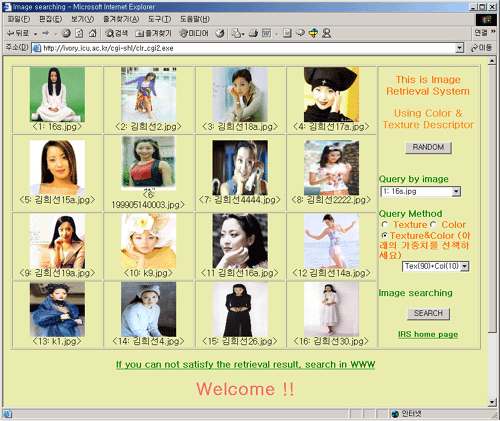
Fig. 6. Retrieval Results with Graphical User Interface
- Conclusion & Future Works
As the requirement of Multimedia Indexing Technology is increasing to retrieve and search for interesting data from huge Internet. Since the traditional retrieval method, which is using textual index, has limitation to handle the multimedia data in current Internet, alternatively, the more efficient representation method is needed. In standard manner, the research for method of feature extraction and multimedia indexing of Audio/Video contents and Images based on MPEG-7 Standard is performing. The feature of content is extracted using MPEG-7 XM(eXperimental Module) for representation of multimedia content. The indexing and matching algorithm using extracted features is researched to support the efficiency of searching and retrieval. To achieve the objectives, MPEG-7 system is being developed, including the user interface and the efficient way for delivering of multimedia description in the mobile Internet environment is also being performed. In the future, the researches will be continued for the more enhanced feature extraction method and meaningful retrieval.